 Four-Stroke engine = Dört zamanlı motor
Four-Stroke engine = Dört zamanlı motorDört zamanlı motorlar (Dört Fazlı), pistonun bir çevriminin (cycle) 4 aşamada (4-stroke cycle) tamamlandığı motor tipleridir. İçten yanmalı motorlar (internal combustion engines) sınıfında yer alırlar.
Wikipedia bilgileri:
 Motorlarda güç üretimi önce yakıtın içindeki kimyasal enerjinin ısı enerjisine dönüşmesi, sonra da bu ısı enerjisinin pistonu harekete geçirmesiyle gerçekleşir. Bir dört zamanlı motorda bu işlem şu aşamaları izler:
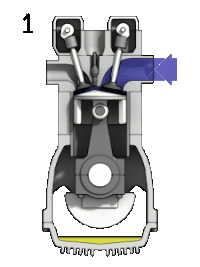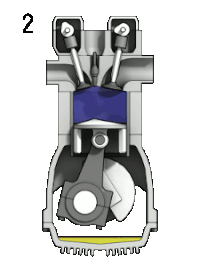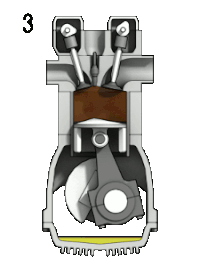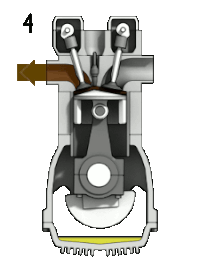
Motorlarda güç üretimi önce yakıtın içindeki kimyasal enerjinin ısı enerjisine dönüşmesi, sonra da bu ısı enerjisinin pistonu harekete geçirmesiyle gerçekleşir. Bir dört zamanlı motorda bu işlem şu aşamaları izler:- 1. Yakıt ve hava karışımı pistonun dışarı hareketiyle dolar.
- 2. Karışım pistonun içeri hareket etmesiyle sıkıştırılır.
- 3. Sıkışmış karışım benzinli motorlarda bir kıvılcım ile tutuşturulur, dizel motorlarda ise yüksek basınç ve sıcaklık altında kendiliğinden tutuşur ve yanma gerçekleşir. Yanma sonucu açığa çıkan enerji ile piston dışarı doğru itilir. Bu sayede krank şaftı döndürülür ve kinetik enerji elde edilmiş olur.
- 4. Pistonun geri dönüşü sırasında egzoz valfı açıktır ve egzoz gazları pistondan atılır. Döngü böylece başlangıç konumuna gelir ve 1. aşamadan itibaren işlemler yinelenir.
Motorun bir döngüsünü yukarıda anlatılan 4 aşamada tamamlamasından dolayı bu tip motorlara 4 zamanlı motorlar ismi verilir. Hareket halindeki benzinli bir araçta bu döngü dakikada ortalama 3.000-3.500 defa tekrarlanır.
İki zamanlı motorlara göre daha verimli olan 4 zamanlı motorlar günümüzde en çok kullanılan içten yanmalı motor tipidir. Ancak imalat aşamasında iki zamanlı motor daha ucuzdur. Fakat iki zamanlı motorun avantajı sadece bu adımda vardır. Çünkü sonrasında (motor üretilip, kullanılacağı makinada kullanılmaya başlandığında), yine dört zamanlı motor avantajlıdır. Çünkü, üstte de yazdığı üzere dört zamanlı motor daha verimlidir. İki zamanlı motorlarda ayrıca:
- Yakıt karışımının bir kısmı yanmadan egzoz gazı ile atıldığı için çevre ve yakıt ekonomisi konularında başarılı değildir.
- Yakıt karışımının pistonun üst kısma ulaşması krank bölümü ile sağlandığından, krank bölümü devamlı yağlamaya maruz değildir ve yağlama yakıt karışımı içine karıştırılan yağ ile olur. Bu yağın yakılması çevre açısından zararlıdır.
- İki strokta çalıştığı için pistonun her yukarı çıkışında yanma olur ve aşırı ısınma meydana gelir.
A four-stroke (also four-cycle) engine is an internal combustion (IC) engine in which the piston completes four separate strokes while turning the crankshaft. A stroke refers to the full travel of the piston along the cylinder, in either direction.
Wikipedia bilgileri:
- Intake: Also known as induction or suction. This stroke of the piston begins at top dead center (T.D.C.) and ends at bottom dead center (B.D.C.). In this stroke the intake valve must be in the open position while the piston pulls an air-fuel mixture into the cylinder by producing vacuum pressure into the cylinder through its downward motion. The piston is moving down as air is being sucked in by the downward motion against the piston.
- Compression: This stroke begins at B.D.C, or just at the end of the suction stroke, and ends at T.D.C. In this stroke the piston compresses the air-fuel mixture in preparation for ignition during the power stroke (below). Both the intake and exhaust valves are closed during this stage.
- Combustion: Also known as power or ignition. This is the start of the second revolution of the four stroke cycle. At this point the crankshaft has completed a full 360 degree revolution. While the piston is at T.D.C. (the end of the compression stroke) the compressed air-fuel mixture is ignited by a spark plug (in a gasoline engine) or by heat generated by high compression (diesel engines), forcefully returning the piston to B.D.C. This stroke produces mechanical work from the engine to turn the crankshaft.
- Exhaust: Also known as outlet. During the exhaust stroke, the piston, once again, returns from B.D.C. to T.D.C. while the exhaust valve is open. This action expels the spent air-fuel mixture through the exhaust valve.
These four strokes can be remembered by the colloquial phrase, "Suck, Squeeze, Bang, Blow".

0 Yorum